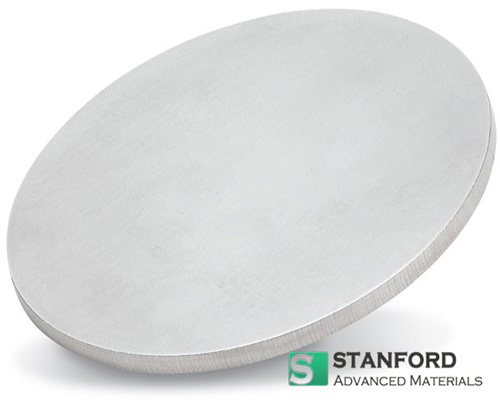
Yttrium Planar Target Description
Stanford Materials Corporation (SMC) provides high-purity Yttrium (Y) Planar Targets, tailored for high-performance thin-film deposition. Yttrium is a rare-earth metal with a high melting point of 1,522°C, excellent oxidation resistance, and robust mechanical strength, making it an ideal material for demanding coating applications. One of its primary benefits is the ability to form a stable oxide layer, which enhances its corrosion resistance and durability, even in high-temperature or reactive environments. Furthermore, yttrium provides excellent adhesion and consistent film deposition, ensuring high-quality coatings with minimal defects.
SMC offers yttrium planar targets in various purities (up to 99.999%), sizes, and custom shapes to meet different sputtering system needs. Our advanced manufacturing process ensures precise composition control, a fine-grain structure, and minimal contamination, optimizing sputtering efficiency and film performance. Whether used for specialized coatings or functional thin films, SMC’s yttrium sputtering targets deliver superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and coating uniformity, making them a trusted choice for cutting-edge industries.
Yttrium Planar Target Specification
- Purity: 99.9~99.99%, ≥99.99%
- Theoretical Density: 4.47 g/cm³
- Melting Point: 1526°C
- Product Shape: Rectangular, or customized upon request
- Product Size: Customized
The above product details are based on theoretical data. For specific requirements and detailed inquiries, please contact us.
Yttrium Planar Target Applications
Yttrium planar sputtering targets are widely used in advanced thin-film deposition due to their excellent oxidation resistance, high-temperature stability, and strong adhesion. One key application is in the electronics and semiconductor industry, where yttrium is used as a protective and insulating layer in microelectronic devices to enhance durability and performance. In optical coatings, yttrium is used to produce high-transparency, anti-reflective, and protective films for lenses, displays, and laser systems. Yttrium is also critical in superconducting thin films, particularly in the development of Yttrium Barium Copper Oxide (YBCO) superconductors, which are vital for energy-efficient electrical systems and advanced research.
Yttrium sputtering targets also play an important role in the aerospace and energy industries, where they are used for thermal barrier coatings to protect components from extreme temperatures and oxidation. In magnetic storage and data recording, yttrium-based thin films enhance stability and performance in hard drives and memory devices. Furthermore, yttrium is used in plasma-resistant coatings for semiconductor fabrication equipment, improving longevity and reliability. With its versatility and high-performance properties, yttrium planar sputtering targets are essential for industries requiring durable, high-quality thin films.
Yttrium Planar Target Packaging
Our products are packed in customized cartons based on material dimensions. Smaller items are securely packed in PP boxes, while larger items are placed in custom wooden crates. We ensure strict adherence to packaging specifications and use appropriate cushioning materials to protect the products during transport.
Packaging Options: Carton, Wooden Box, or Customized.
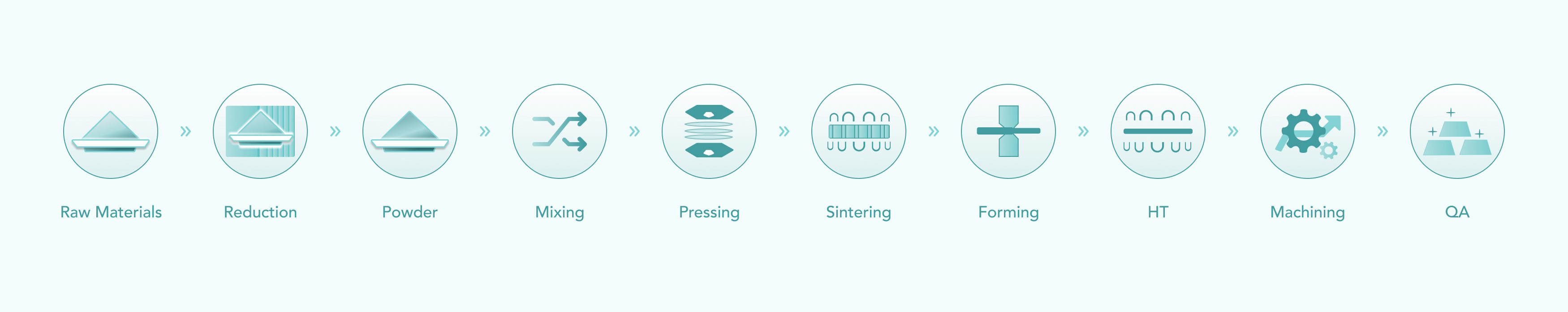
Manufacturing Process
- Brief Manufacturing Process Flow
- Testing Method
- Chemical Composition Analysis: Verified using techniques such as GDMS or XRF to ensure purity compliance.
- Mechanical Properties Testing: Includes tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation tests to evaluate material performance.
- Dimensional Inspection: Measures thickness, width, and length to ensure tolerance compliance.
- Surface Quality Inspection: Checks for defects such as scratches, cracks, or inclusions through visual and ultrasonic examination.
- Hardness Testing: Assesses material hardness to confirm uniformity and mechanical reliability.
Yttrium Planar Target FAQs
Q1: What are the advantages of using yttrium in thin-film coatings?
A1: Yttrium offers excellent oxidation resistance, high thermal stability, strong adhesion, and uniform film deposition, making it ideal for use in electronics, optics, and superconductors.
Q2: Can yttrium planar targets be customized in size and shape?
A2: Yes, we offer customized sizes, shapes, and bonding options to meet specific sputtering system requirements.
Q3: How should yttrium sputtering targets be stored and handled?
A3: Yttrium is sensitive to oxidation, so it should be stored in a dry, clean environment and handled carefully to avoid contamination or damage.
Performance Comparison Table with Competitive Products
| Feature |
Yttrium Rotary Target |
Yttrium Planar Target |
| Material Utilization |
Up to 80-90% |
Around 30-40% |
| Service Life |
Longer, reducing replacement frequency |
Shorter, requiring more frequent replacement |
| Coating Uniformity |
More uniform, ideal for large-area coatings |
May have thickness variations |
| Production Cost |
Higher initial cost but more economical long term |
Lower initial cost but requires more frequent changes |
| Applications |
Large-area coatings (TFT-LCD, solar cells, optical coatings) |
Small-area coatings (semiconductors, precision electronics) |
| Sputtering Stability |
More stable, reducing material loss |
Potentially less stable due to uneven erosion |
| Compatible Equipment |
Requires rotary sputtering systems |
Compatible with traditional planar sputtering systems |
Related Information
- Raw Materials-Yttrium
Yttrium (Y) is a rare-earth metal with atomic number 39 and atomic weight 88.91. It is a silvery-white, ductile, and relatively stable metal that does not tarnish easily in air due to the formation of a protective oxide layer. Yttrium has a high melting point of 1,522°C (2,772°F) and exceptional thermal and electrical properties, making it invaluable in advanced material applications.
Although classified as a rare-earth element, yttrium is relatively abundant in the Earth’s crust and is commonly found in minerals such as xenotime, monazite, and bastnäsite. Its unique properties make it essential in electronics, superconductors, optical coatings, and high-temperature structural materials. Yttrium is heavily used in the production of Yttrium Barium Copper Oxide (YBCO) superconductors, phosphors for LED and CRT displays, and specialized alloys for aerospace applications.
With its outstanding oxidation resistance, stability, and ability to enhance material properties, yttrium continues to be a crucial element in modern technology and scientific research.